Top Safety Features Every Industrial Chemical Reactor Must Have
Industrial chemical reactors are at the heart of countless industries—from pharmaceuticals and petrochemicals to food processing and specialty chemicals. These highly engineered reaction vessels allow complex chemical reactions to occur under controlled conditions of temperature, pressure, and mixing.
However, chemical processes are often hazardous, involving flammable solvents, corrosive chemicals, exothermic reactions, or high pressures. Without proper safety features, a reactor can quickly become a source of catastrophic accidents, leading to financial losses, regulatory penalties, or even loss of life.
This makes safety design in chemical reactors absolutely non-negotiable. In this blog, we’ll explore the top safety features every industrial chemical reactor must have, their importance, and how they ensure smooth, compliant, and accident-free operations.
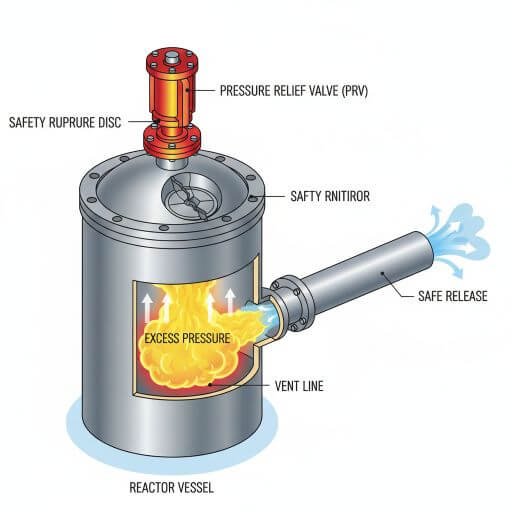
1. Pressure Relief Systems
Why It Matters:
Many chemical reactions generate gases or involve pressurized systems. Over-pressurization can lead to vessel rupture or explosions if not controlled.
Key Features:
Safety Relief Valves (SRVs): Open automatically when internal pressure exceeds design limits.
Rupture Discs: A fail-safe that bursts at a set pressure to release excess pressure instantly.
Venting Systems: Safe discharge pathways to prevent toxic gas release into the workplace.
Example: In pharmaceutical batch reactors, relief valves ensure safe handling of sudden gas evolution during exothermic reactions.
2. Emergency Shutdown Systems (ESD)
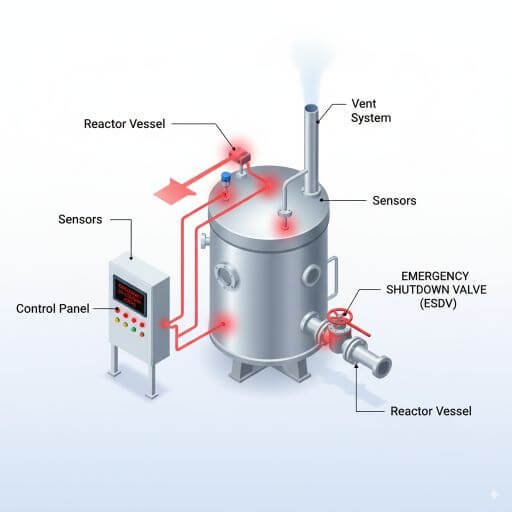
Why It Matters:
Chemical processes can change rapidly—reactions may accelerate, equipment may fail, or utilities may be disrupted.
Key Features:
Automated shutdown controls triggered by abnormal conditions.
Manual emergency stop switches accessible to operators.
Isolation valves to stop reactant feed and contain hazards.
Best Practice: Linking the ESD system with PLC/SCADA automation ensures real-time monitoring and instant reaction.
3. High-Precision Temperature Control
Why It Matters:
Most chemical reactors are highly temperature-sensitive. Uncontrolled temperature rises in exothermic reactions can cause thermal runaway, fires, or explosions.
Safety Features:
Jacketed Reactors & Limpet Coils for efficient heating/cooling.
Temperature Sensors & Alarms for continuous monitoring.
Automated Cooling Systems that activate instantly during overheating.
Example: In API manufacturing, glycol-cooled jacketed reactors prevent overheating during synthesis.

4. Pressure and Vacuum Monitoring
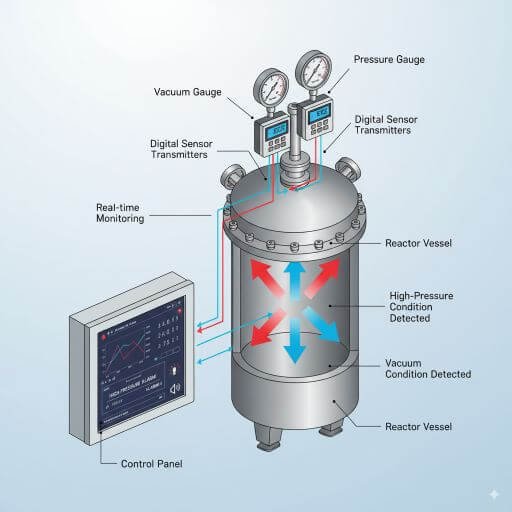

Why It Matters:
Both high-pressure and vacuum operations are common in chemical processing. A sudden pressure drop or spike can indicate leaks, blockages, or dangerous reaction deviations.
Safety Features:
Digital pressure transmitters for precise monitoring.
Vacuum breakers to protect vessels during cleaning or unloading.
Alarm systems to notify operators of unsafe pressure fluctuations.
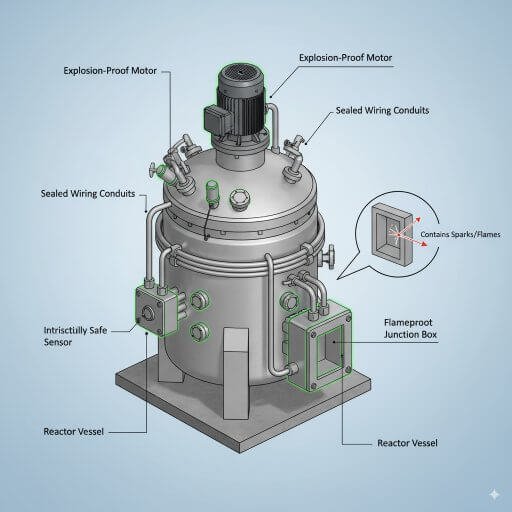
5. Explosion-Proof Electrical Systems
Why It Matters:
Many chemical processes involve flammable vapors. A single spark from electrical systems can trigger explosions.
Safety Features:
Flameproof motors for agitators and pumps.
Intrinsically safe instruments for monitoring.
Grounding and earthing systems to prevent static charge buildup.
Compliance Standard: ATEX and IECEx certifications for explosion-proof design.
6. Agitator Safety Features
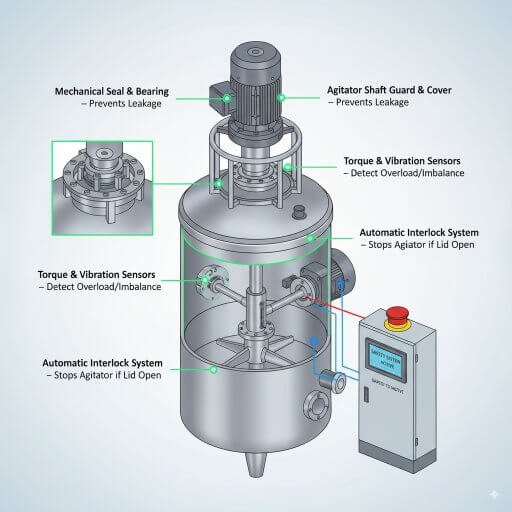
Why It Matters:
Agitators are essential for mixing but can cause hazards if not designed properly. Over-speed, seal leaks, or shaft failures can compromise safety.
Key Features:
Mechanical seals to prevent leakage of toxic or flammable materials.
Over-torque protection to avoid shaft damage.
Agitator interlocks to prevent accidental start-up during maintenance.
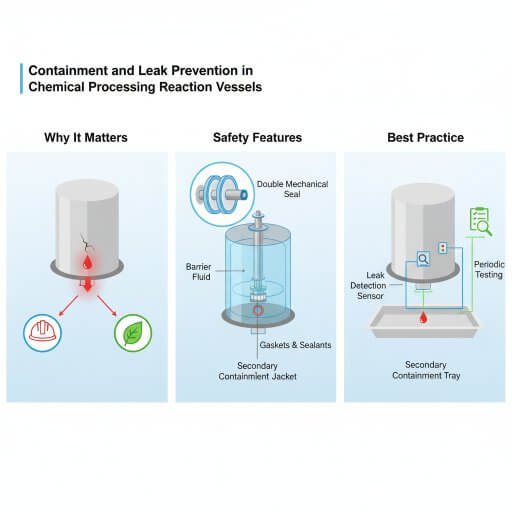
7. Containment and Leak Prevention
Why It Matters:
Leaks of hazardous chemicals not only harm workers but can contaminate the environment.
Safety Features:
Double mechanical seals for agitator shafts.
Secondary containment jackets for highly toxic materials.
Proper gaskets and sealants compatible with process chemicals.
Best Practice: Periodic leak detection testing for seals and joints.
8. Fire and Explosion Suppression Systems
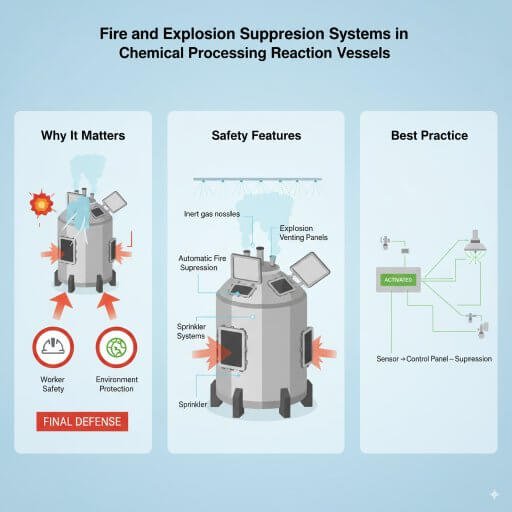
Why It Matters:
Even with all precautions, fires and explosions can still occur. Suppression systems act as the final defense.
Safety Features:
Automatic fire suppression with inert gases or water sprays.
Explosion venting panels to safely release blast pressure.
Sprinkler systems around the reactor area.
9. Automation, Control & Alarms
Why It Matters:
Human error is a leading cause of accidents. Automated monitoring and alarm systems reduce risks.
Key Features:
PLC/SCADA systems for real-time monitoring.
Alarm hierarchy (visual, audible, emergency cut-off).
Redundant sensors for critical parameters like temperature and pressure.
Future Trend: AI-driven predictive analytics to detect abnormal reaction patterns before they escalate.

10. Clean-in-Place (CIP) and Sterilize-in-Place (SIP) Systems

Why It Matters:
Residues from previous batches can cause contamination, uncontrolled reactions, or even fires.
Safety Features:
Automated CIP systems that flush vessels without manual intervention.
SIP with steam sterilization for pharmaceutical and food applications.
Validation protocols to ensure repeatable cleaning efficiency.
11. Operator and Environmental Safety Systems
Beyond equipment safety, protecting people and the environment is crucial.
Features:
Gas detectors for flammable or toxic vapors.
Fume extraction systems to control airborne hazards.
Secondary containment bunds to prevent spillage accidents.
Safety interlocks that prevent reactor operation if safety doors are open.

12. Compliance with Safety Standards

Chemical reactors must adhere to international safety codes:
ASME Section VIII – Pressure vessel design.
API Standards – For petrochemical reactors.
GMP & FDA Regulations – For pharmaceutical reactors.
OSHA & HSE Guidelines – Workplace safety compliance.
13. Case Studies: Safety in Action
Case 1: Explosion Prevention in a Petrochemical Reactor
A petrochemical plant handling flammable solvents installed double mechanical seals and flameproof motors. This prevented ignition even during a major solvent leak.
Case 2: Overheating Controlled in a Pharmaceutical API Reactor
During API synthesis, an exothermic reaction led to a sudden heat spike. The automated cooling system activated instantly, preventing thermal runaway.

14. Future Trends in Reactor Safety

IoT-enabled smart reactors with predictive maintenance.
AI-powered hazard detection in real-time.
Green chemistry reactors with safer, eco-friendly processes.
Digital twin simulation for safety testing before plant-scale operations.
The safety of an industrial chemical reactor is not optional—it’s the foundation of reliable and compliant operations. From pressure relief systems and explosion-proof designs to CIP/SIP cleaning and advanced automation, each feature plays a vital role in preventing accidents and ensuring operator well-being.
Companies that invest in high-quality, safety-focused reaction vessels not only protect their workforce and assets but also gain a competitive edge by meeting regulatory requirements and earning customer trust.
When it comes to chemical processing, remember: safety isn’t an added feature—it’s the core design principle.

